WordPress is the world’s most widely used content management system (CMS), powering over 800 million websites globally and accounting for approximately 40% of all indexable websites. It is a highly customisbale open-source platform, making it accessible to both experienced developers and beginners, whether for personal blogs, business websites, large-scale online stores or web apps.
This Article Will Cover:
- Introduction
- What is the Latest WordPress Version
- Why You Should Always Update to the Latest WordPress Version
- How to Check Your Current WordPress Version
- 2. Look at the Admin Footer
- How to Check for WordPress Updates
- Precautions Before Updating WordPress
- Risks of Auto-Updating WordPress
- What’s the Safer Alternative?
- Troubleshooting WordPress Update Issues
- Conclusion
Introduction
As an open-source platform with a vast user base, WordPress frequently releases updates aimed at enhancing security, performance, and compatibility with themes and plugins. Keeping your WordPress installation updated is essential for speed, security, and functionality, protecting your site from vulnerabilities and maintaining a healthy website.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the latest WordPress version, including how to check your current version, understand the benefits of updating, and safely apply updates without disrupting your website.
What is the Latest WordPress Version
Each WordPress update introduces new features, bug fixes, and security patches to enhance the platform’s functionality.
- The current stable version of WordPress is regularly updated to keep up with modern web standards and security best practices.
- WordPress follows a version numbering system where major updates introduce new features and minor updates focus on security patches and bug fixes.
- The latest version of WordPress typically includes improvements to the Gutenberg block editor, performance enhancements, theme customisation features, and security updates.
- If a new beta version is available, it is intended for testing and should not be used on live websites.
Checking the official WordPress release page is the best way to stay informed about the latest version.
Why You Should Always Update to the Latest WordPress Version
Updating WordPress regularly is required for maintaining the security, speed, and overall health of your website. Here’s why:
1. Security Enhancements
WordPress is an open-source platform, meaning its code is publicly available. This transparency allows developers to contribute to improvements, but it also makes WordPress a target for hackers. Each update includes security patches to fix vulnerabilities and protect your site from attacks.
2. Performance & Speed Improvements
With each update, WordPress introduces optimisations that improve page loading speed, database efficiency, and code performance. Faster websites rank higher on search engines and provide a better user experience.
3. Compatibility with Themes and Plugins
Developers of themes and plugins frequently update their software to work with the latest WordPress version. Running an outdated version of WordPress can cause compatibility issues, leading to broken features or errors on your website.
4. New Features & Improved User Experience
WordPress regularly enhances the Gutenberg editor, theme customisation options, and other usability features. By updating, you gain access to the latest tools that can improve your workflow and website functionality.
5. Bug Fixes
Every update includes fixes for known issues from previous versions. Keeping your WordPress installation up to date helps your website operate smoothly without errors or glitches. Or at least reducing those risks.
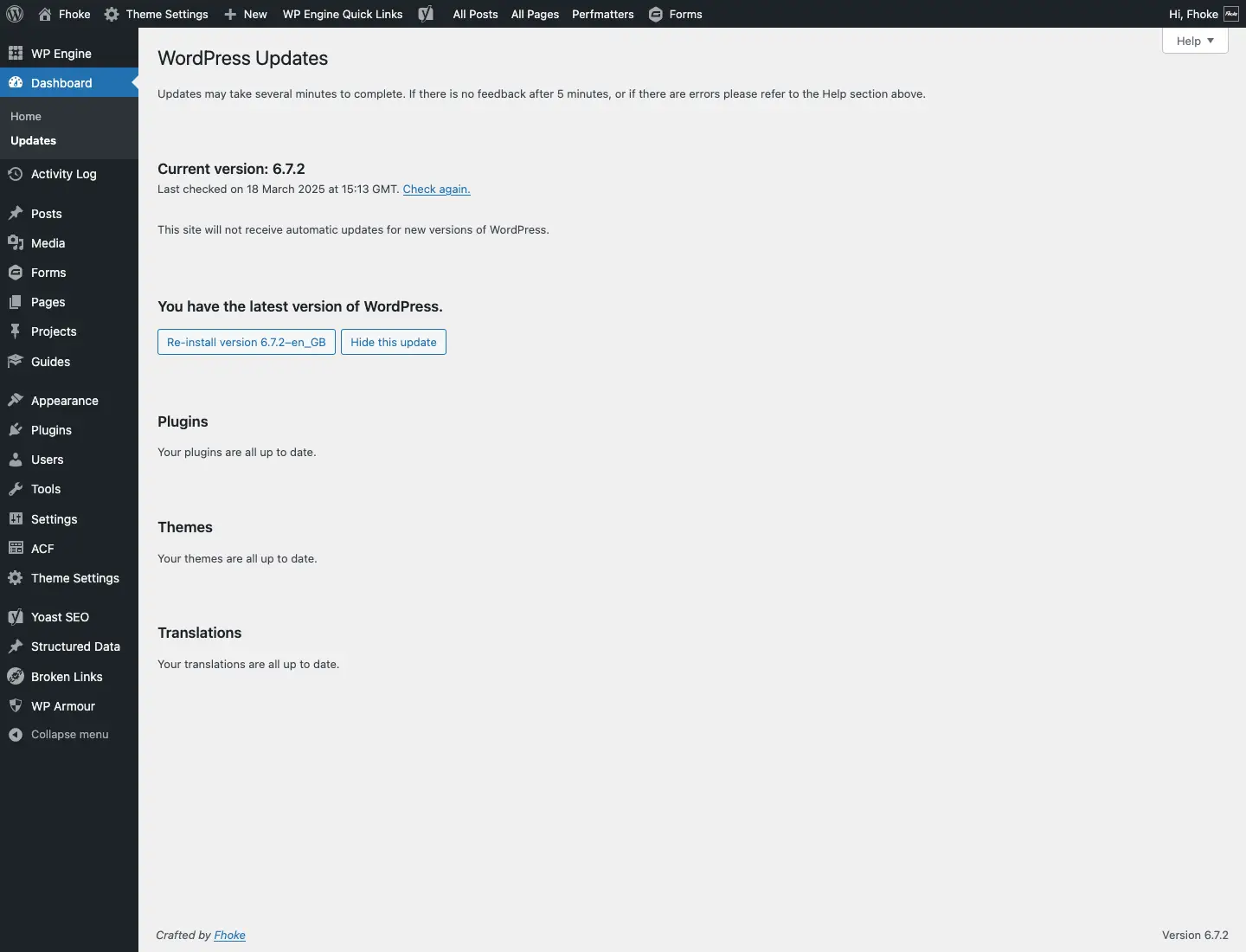
How to Check Your Current WordPress Version
Before updating, check which WordPress version your site is running. Here are several ways to do this:
1. Check from the WordPress Dashboard
- Log in to your WordPress admin panel.
- Navigate to Dashboard > Updates.
- The page will display your current version and notify you if an update is available.
2. Look at the Admin Footer
- Scroll to the bottom of any admin panel page.
- You will see the WordPress version number displayed in the footer.
3. Use the Site Health Tool
- Go to Tools > Site Health.
- The tool provides details about your WordPress version and any recommended updates.
4. Check via File Manager or cPanel
- Access your website’s File Manager or cPanel.
- Locate the wp-includes/version.php file and open it.
- Look for the line that specifies $wp_version = ‘X.X.X’.
5. Use an Online WordPress Version Checker
Some online tools allow you to check a website’s WordPress version by entering its URL.
Note: This method may not always work if version-hiding techniques are applied for security reasons.
How to Check for WordPress Updates
WordPress automatically checks for updates and displays them in the Dashboard > Updates section. However, if no update appears, try the following:
- Manually refresh the updates page by clicking “Check Again”.
- Clear your browser cache and WordPress site cache.
- Disable conflicting plugins that might interfere with update detection.
How to Update WordPress to the Latest Version
Updating WordPress is straightforward, but it is important to do it correctly to avoid issues.
Method 1: Automatic Updates
- WordPress applies automatic updates for minor security releases.
- You can enable automatic updates for major releases by adding this line to wp-config.php:
define( 'WP_AUTO_UPDATE_CORE', true );Method 2: Manual Updates via WordPress Dashboard
- Go to Dashboard > Updates and click “Update Now”.
- WordPress will download and install the latest version automatically.
Method 3: Updating WordPress Manually via FTP
- Download the latest WordPress version from wordpress.org.
- Use an FTP client (like FileZilla) to upload the new files to your server.
- Overwrite existing files and then run the database update when prompted.

Precautions Before Updating WordPress
Before updating, take the following precautions:
- Backup Your Website (Use your hosting provider’s backup service, a manual backup, or a plugin like UpdraftPlus).
- Test Updates on a Staging Site before applying them to your live website.
- Confirm Theme & Plugin Compatibility to avoid breaking your website.
- Check PHP Version – WordPress recommends PHP 7.4 or higher for best performance.
Risks of Auto-Updating WordPress
While auto-updates for WordPress plugins and themes seem convenient, they can introduce several potential risks that may impact your website’s stability, security, and performance.
This is why major website updates should be done during ‘office hours’ so you can get support when you need it.
The following outlines the potential problem you could encounter, and it may be worth creating a contingency plan in the event something does go wrong. This might be as simple as calling your WordPress Agency (like ours) or internal IT department, or for a smaller website, sending a panicked email to your local website developer. In any case, it’s good to know who to call at a time of need.
1. Compatibility Issues
- Major updates can sometimes cause plugins and themes to become incompatible with the latest WordPress version.
- If critical components stop working, this can lead to broken functionality, design issues, or even complete site failure.
2. Security Vulnerabilities
- While updates are intended to fix security vulnerabilities, auto-updates can introduce new risks if they contain a flaw.
- If a plugin or theme update has an undiscovered security weakness, auto-updating means the vulnerability is immediately active on your site.
3. Loss of Customisations
- If you manually customise a theme or plugin without a child theme, an update can overwrite your changes, leading to lost functionality or altered designs.
- This is particularly problematic for businesses that rely on custom-built features.
4. Difficult Troubleshooting
- When multiple auto-updates happen at once, it becomes challenging to pinpoint which update caused an issue.
- Debugging errors requires manually rolling back updates one by one, which can be time-consuming.
5. False Sense of Security
- Enabling auto-updates can create a false sense of security, where site owners assume their website is always safe and optimised.
- In reality, auto-updates can fail without notification, leading to outdated and vulnerable software being left unchecked.
6. Data Loss and Lack of Control
- One of the risks of auto-updating WordPress is the lack of control over when updates are applied, which can sometimes lead to data loss or unexpected downtime. In rare cases, an update may corrupt the database or result in lost content, making recovery difficult and time-consuming without a proper backup system in place.
- Further, as auto-updates happen without user intervention, they can happen at high-traffic periods or conflict with critical site functions, potentially causing unexpected site outages. This lack of oversight can disrupt user experience and business operations, making it necessary to manage updates manually or use a staging environment for testing before applying changes to a live site.
7. SEO Impact
- If a theme or plugin update breaks key SEO-related functions (such as metadata, structured data, or caching), it can negatively impact search engine rankings.
- Updates can also alter site speed, affecting Core Web Vitals and overall SEO performance.
- Much of what contributes to strong SEO operates behind the scenes, making it difficult to detect issues at a glance. As a result, SEO problems can develop without the website owner realising, potentially affecting rankings and visibility over time. This is why having an SEO expert to monitor and analyse your website’s performance can be invaluable, guaranteeing that any issues are identified and addressed before they cause significant harm.
What’s the Safer Alternative?
If you are responsible for the maintenance of your website, to avoid the risks associated with auto-updates, consider:
- Outsourcing your website hosting/management to a reputable WordPress Agency or Developer who can take on the responsibility. At Fhoke we host over 150 client websites, so we’d like to think we know what we’re doing.
- Manually reviewing and updating WordPress, themes, and plugins on a scheduled basis is advised.
- Testing updates on a staging site before applying them to a live website.
- Using a managed WordPress hosting provider that handles updates with rollback options.
- Enabling selective auto-updates for minor security fixes while keeping major updates manual.
By taking a controlled approach to updates, you can ensure your website remains secure, functional, and optimised without the risks of unexpected auto-updates.
Troubleshooting WordPress Update Issues
If You Experience Issues After Updating, Try These Solutions:
Updating WordPress is usually a smooth process, but occasionally, issues may arise that can affect your website’s functionality. If you experience problems after updating, here are some troubleshooting steps to help you quickly identify and resolve them:
1. Check for Plugin or Theme Conflicts
If your website breaks after an update, a plugin or theme may be incompatible with the latest WordPress version.
Solution: Deactivate all plugins and switch to a default WordPress theme (such as Twenty Twenty-Four). Reactivate each plugin one by one to pinpoint the issue.
2. Fix the White Screen of Death (WSOD)
If your site only displays a blank white screen, this usually indicates a PHP error or memory limit issue.
Solution: Increase PHP memory in wp-config.php by adding:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');If the issue persists, check the error logs in your hosting panel for more details.
3. Resolve Update Failure or Incomplete Installation
If the update was interrupted or only partially installed, it may cause missing files or database errors.
Solution: Manually reinstall WordPress by downloading the latest version from WordPress.org and replacing your core files via FTP or File Manager (excluding the wp-content folder).
4. Restore from Backup if Necessary
If an update causes significant problems, reverting to a previous backup can quickly restore functionality.
Solution: If you have a backup or manual backup from your hosting provider, restore it to bring your site back to its previous working state. That’s why making a back-up before updating is a good idea.
5. Check File and Folder Permissions
Incorrect file permissions can cause errors or prevent WordPress from updating correctly.
Solution: Set file permissions to 644 for files and 755 for folders using your hosting File Manager or FTP client.
6. Manually Clear Cache and Browser Data
Sometimes, cached files from your browser or a caching plugin may cause display errors after an update.
Solution: Clear your browser cache, and if using a caching plugin (e.g., WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache), clear the site’s cache through the plugin settings.
7. Check Error Logs for More Information
If you are unsure what is causing the issue, check your server’s error logs for details.
Solution: Enable WP_DEBUG mode in wp-config.php to display errors:
define('WP_DEBUG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false); This will log errors in wp-content/debug.log, helping you diagnose the problem.
8. Contact Your Hosting Provider for Assistance
If you cannot identify or resolve the issue, your web hosting provider may be able to help.
Solution: Reach out to your host’s support team for assistance with server logs, resource limits, or rollback options.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can quickly resolve issues caused by WordPress updates and ensure your site remains stable and functional.
Conclusion
Keeping WordPress updated is important for security, speed, and compatibility. Following the steps in this guide can keep your site safe and fully optimised. Regularly checking your WordPress version and applying updates will help you maintain a secure and high-performing website.
If you are unsure about updating WordPress yourself, consider getting in touch with our team. We host over 150 client sites and have been working with WordPress since 2008. Failing that, use a staging environment to test updates first before applying them to your live site. Reading up and staying ahead of WordPress updates will help you decide whether to upgrade immediately or hold off for a few days.
Most hosting providers, such as WP Engine and Flywheel, will roll out these updates for you after checking the compatibility of the changes first. This gives WordPress developers plenty of time to patch bugs and plugins as they tend to wait a few days, sometimes weeks.